Wednesday, 28 August 2013
Sunday, 4 August 2013
WHY CAPTCHA???
Okay , lets know it
What is CAPTCHA?
CAPTCHA, an acronym that stands for Completely Automated Public Turing Test to Tell Computers and Humans Apart. They're also known as a type of Human Interaction Proof (HIP).CAPTCHA is used to make sure that the entity filling out a form, commenting on a blog, or registering for a website is an actual person instead of a bot trying to spam the site.
Types of CAPTCHAs
1. The Standard Distorted Word CAPTCHA with an Audio Option
This comes from the most popular CAPTCHA company out there, ReCAPTCHA. It is reliable, but some of the distorted word images are rather hard to solve. To get past that it allows you the option to “reCAPTCHA,” in order to receive a new one. There is also an audio option if you are unable to visually make out the word.
2. Picture Identification CAPTCHA

This CAPTCHA by Picatcha provides the user with an elementary choice of choosing the correct image that they are asked to identify. They never get harder than basic images so you won’t have to worry too much about your users not being able to depict the difference between them and the incorrect images.
3. Math Solving CAPTCHA
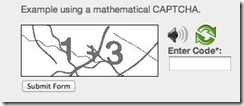
If your users can’t solve these basic math problems then maybe you don’t want them commenting on your threads anyways. These provide you with easy to read numbers that must be added in order to get past the CAPTCHA.
4. 3D CAPTCHA

This one may be one of the more difficult ones to solve, but it is sure to keep out robotic predators. There are several types of three dimensional CAPTCHAs including both images and words. They call it the “super-CAPTCA.”
5. Ad-Injected CAPTCHA

If your users are spending a few seconds everyday on CAPTCHAs why not earn some extra cash for your website? This may seem iffy for the brand as they are associating themselves with a rather annoying process, but it does make sense in terms of brand recognition. This particular example is of the main company providing this known as Solve Media. Publishers get paid on a 60/40 split with Solve Media (Solve Media taking 60%) on a per solve/impression basis.
Applications of CAPTCHAs
CAPTCHAs have several applications for practical security, including (but not limited to):· Preventing Comment Spam in Blogs. Most bloggers are familiar with programs that submit bogus comments, usually for the purpose of raising search engine ranks of some website (e.g., "buy penny stocks here"). This is called comment spam. By using a CAPTCHA, only humans can enter comments on a blog. There is no need to make users sign up before they enter a comment, and no legitimate comments are ever lost!
· Protecting Website Registration. Several companies (Yahoo!, Microsoft, etc.) offer free email services. Up until a few years ago, most of these services suffered from a specific type of attack: "bots" that would sign up for thousands of email accounts every minute. The solution to this problem was to use CAPTCHAs to ensure that only humans obtain free accounts. In general, free services should be protected with a CAPTCHA in order to prevent abuse by automated scripts.
· Protecting Email Addresses From Scrapers. Spammers crawl the Web in search of email addresses posted in clear text. CAPTCHAs provide an effective mechanism to hide your email address from Web scrapers. The idea is to require users to solve a CAPTCHA before showing your email address.
· Online Polls. In November 1999, http://www.slashdot.org released an online poll asking which was the best graduate school in computer science (a dangerous question to ask over the web!). As is the case with most online polls, IP addresses of voters were recorded in order to prevent single users from voting more than once. However, students at Carnegie Mellon found a way to stuff the ballots using programs that voted for CMU thousands of times. CMU's score started growing rapidly. The next day, students at MIT wrote their own program and the poll became a contest between voting "bots." MIT finished with 21,156 votes, Carnegie Mellon with 21,032 and every other school with less than 1,000. Can the result of any online poll be trusted? Not unless the poll ensures that only humans can vote.
· Preventing Dictionary Attacks. CAPTCHAs can also be used to prevent dictionary attacks in password systems. The idea is simple: prevent a computer from being able to iterate through the entire space of passwords by requiring it to solve a CAPTCHA after a certain number of unsuccessful logins. This is better than the classic approach of locking an account after a sequence of unsuccessful logins, since doing so allows an attacker to lock accounts at will.
· Search Engine Bots. It is sometimes desirable to keep webpages unindexed to prevent others from finding them easily. There is an html tag to prevent search engine bots from reading web pages. The tag, however, doesn't guarantee that bots won't read a web page; it only serves to say "no bots, please." Search engine bots, since they usually belong to large companies, respect web pages that don't want to allow them in. However, in order to truly guarantee that bots won't enter a web site, CAPTCHAs are needed.
· Worms and Spam. CAPTCHAs also offer a plausible solution against email worms and spam: "I will only accept an email if I know there is a human behind the other computer." A few companies are already marketing this idea.
references
-http://www.findexamples.com
Many of us many times visited many web pages filled many web forms in the Websites filled many CAPTCHA challenges but do you know why CAPTCHA ?
Okay , lets know it
What is CAPTCHA?
CAPTCHA, an acronym that stands for Completely Automated Public Turing Test to Tell Computers and Humans Apart. They're also known as a type of Human Interaction Proof (HIP).CAPTCHA is used to make sure that the entity filling out a form, commenting on a blog, or registering for a website is an actual person instead of a bot trying to spam the site.
Types of CAPTCHAs
1. The Standard Distorted Word CAPTCHA with an Audio Option![clip_image004[4] clip_image004[4]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEjA9oR4z-kwrH6GwCl2LBclSKepgjTRWkDUgPQ_Ghjs6dbTKocCXP5U1JCJiFub5CndSNAefY97YMwYLiamdF85YMYb_iqhLnieg4mH1_2DsdWVVtNLJ_O896lY3fqfgkb7pKFNy7neTWPj/?imgmax=800)
This comes from the most popular CAPTCHA company out there, ReCAPTCHA. It is reliable, but some of the distorted word images are rather hard to solve. To get past that it allows you the option to “reCAPTCHA,” in order to receive a new one. There is also an audio option if you are unable to visually make out the word.
2. Picture Identification CAPTCHA
![clip_image006[4] clip_image006[4]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEiXz7TBDWG2fQVY14CTDNBDMZHxASLRD-uXp8lrtJwsvyv4-z3WtmKoBRLsjxsdOxGOtp7_9R8ELTUy0nrqXQlJtawoltvgWN8Qc1L2PosyQ3jWiwTb6MMzxSYZZqswmtp3c53ZcKLB9a79/?imgmax=800)
This CAPTCHA by Picatcha provides the user with an elementary choice of choosing the correct image that they are asked to identify. They never get harder than basic images so you won’t have to worry too much about your users not being able to depict the difference between them and the incorrect images.
3. Math Solving CAPTCHA
![clip_image008[4] clip_image008[4]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgnp2ksj0WoR5DdcUKHwyAhDqt7PGiKRhaX8dRSuhT6KuqhrCtfwwYJB0FWgqdwTOHsgVEuwOJOM68YTRKxPfvbbVpG76Fgz0vzrTk2u2_TlfRluSIKmvOGiifXB117XSBAxV7ft2kY6xmZ/?imgmax=800)
If your users can’t solve these basic math problems then maybe you don’t want them commenting on your threads anyways. These provide you with easy to read numbers that must be added in order to get past the CAPTCHA.
4. 3D CAPTCHA
![clip_image010[4] clip_image010[4]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhSjW7a0yG2XwNuajtgdTtzrme1fWp5bR8nGecjYPe14WDr3W_yzF0EqXoOJmaI-NeAOVRXGEZBhmR5iXSgnXGTQ2iqsUt-wbp3DrULTGHTt4gUKeHDp3j20loAtRhV4AMH6FJnR5VlZOSq/?imgmax=800)
This one may be one of the more difficult ones to solve, but it is sure to keep out robotic predators. There are several types of three dimensional CAPTCHAs including both images and words. They call it the “super-CAPTCA.”
5. Ad-Injected CAPTCHA
![clip_image011[4] clip_image011[4]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEi5HlHMyIiNQ3ewykxx9QGmKHy73PO-y9OGTYjaDWjCTPzlQBTBzTdM8lVokVXLRA_-LE3SicLI067tXoubYfIMdKoUi5WsHB7zHZDqe6So_FqX7-20bcjGBc3qjhHvNJM5SRTm2nV3Sm8f/?imgmax=800)
If your users are spending a few seconds everyday on CAPTCHAs why not earn some extra cash for your website? This may seem iffy for the brand as they are associating themselves with a rather annoying process, but it does make sense in terms of brand recognition. This particular example is of the main company providing this known as Solve Media. Publishers get paid on a 60/40 split with Solve Media (Solve Media taking 60%) on a per solve/impression basis.
Applications of CAPTCHAs
CAPTCHAs have several applications for practical security, including (but not limited to):· Preventing Comment Spam in Blogs. Most bloggers are familiar with programs that submit bogus comments, usually for the purpose of raising search engine ranks of some website (e.g., "buy penny stocks here"). This is called comment spam. By using a CAPTCHA, only humans can enter comments on a blog. There is no need to make users sign up before they enter a comment, and no legitimate comments are ever lost!
· Protecting Website Registration. Several companies (Yahoo!, Microsoft, etc.) offer free email services. Up until a few years ago, most of these services suffered from a specific type of attack: "bots" that would sign up for thousands of email accounts every minute. The solution to this problem was to use CAPTCHAs to ensure that only humans obtain free accounts. In general, free services should be protected with a CAPTCHA in order to prevent abuse by automated scripts.
· Protecting Email Addresses From Scrapers. Spammers crawl the Web in search of email addresses posted in clear text. CAPTCHAs provide an effective mechanism to hide your email address from Web scrapers. The idea is to require users to solve a CAPTCHA before showing your email address.
· Online Polls. In November 1999, http://www.slashdot.org released an online poll asking which was the best graduate school in computer science (a dangerous question to ask over the web!). As is the case with most online polls, IP addresses of voters were recorded in order to prevent single users from voting more than once. However, students at Carnegie Mellon found a way to stuff the ballots using programs that voted for CMU thousands of times. CMU's score started growing rapidly. The next day, students at MIT wrote their own program and the poll became a contest between voting "bots." MIT finished with 21,156 votes, Carnegie Mellon with 21,032 and every other school with less than 1,000. Can the result of any online poll be trusted? Not unless the poll ensures that only humans can vote.
· Preventing Dictionary Attacks. CAPTCHAs can also be used to prevent dictionary attacks in password systems. The idea is simple: prevent a computer from being able to iterate through the entire space of passwords by requiring it to solve a CAPTCHA after a certain number of unsuccessful logins. This is better than the classic approach of locking an account after a sequence of unsuccessful logins, since doing so allows an attacker to lock accounts at will.
· Search Engine Bots. It is sometimes desirable to keep webpages unindexed to prevent others from finding them easily. There is an html tag to prevent search engine bots from reading web pages. The tag, however, doesn't guarantee that bots won't read a web page; it only serves to say "no bots, please." Search engine bots, since they usually belong to large companies, respect web pages that don't want to allow them in. However, in order to truly guarantee that bots won't enter a web site, CAPTCHAs are needed.
· Worms and Spam. CAPTCHAs also offer a plausible solution against email worms and spam: "I will only accept an email if I know there is a human behind the other computer." A few companies are already marketing this idea.
references
-http://www.findexamples.com
-http://www.CAPTCHA.net/
-http://c2.com/cgi/wiki?CAPTCHATest
-http://www.howstuffworks.com
-http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CAPTCHA
-http://www.CAPTCHA.net/
-http://c2.com/cgi/wiki?CAPTCHATest
-http://www.howstuffworks.com
-http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CAPTCHA
Ethical hacking
Contents:
1. What is hacking?
2. What is Ethical hacking?
3. History of Hacking
4. Types of hackers
5. Hacking methods
6. What do Ethical hackers do?
7. Ethical hacking process
8. The pros of ethical hacking
9. The cons of ethical hacking
1. What is hacking?
The simple definition of hacking is the unconventional way of using system which we are not supposed to use. It means hacking is to expand the capabilities of any electronic device to use them beyond the original intentions of the manufacturer.

Computer hacking is the most popular form of hacking nowadays, especially in the field of computer security, but hacking exists in many other forms, such as phone hacking, brain hacking, etc. and it's not limited to either of them.
2. What is ethical hacking?
The work of ethical hacking is still considered hacking because it uses knowledge of computer systems in an attempt to in some way penetrate them or crash them. This work is ethical because it is performed to increase the safety of the computer systems.
3. History of hacking
As a matter of fact, the first hackers appeared in the 1960's at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), and their first victims were electric trains. They wanted them to perform faster and more efficiently. So, is hacking always bad? Not really. It only depends on how to use it.
During the 1970's, a different kind of hacker appeared: the perhaps or phone hackers. They learned ways to hack the telephonic system and make phone calls for free. John Draper, built a blue box that could do this and the Esquire magazine published an article on how to build them. Fascinated by this discovery, two kids, Steve Wozniak and Steve Jobs, decided to sell these blue boxes, starting a business friendship which resulted in the founding of Apple.
By the 1980's, phreaks started to migrate to computers, and the first Bulletin Board Systems (BBS) appeared. BBS are like the yahoo groups of today, were people posted messages of any kind of topics. The BBS used by hackers specialized in tips on how to break into computers, how to use stolen credit card numbers and share stolen computer passwords.
During the 1990's, when the use of the internet widespread around the world, hackers multiplied, but it wasn't until the end of the decade that system's security became mainstream among the public.
Today, we are accustomed to hackers, crackers, viruses, Trojans, worms and all of the techniques we need to follow to combat them.
4. Types of hackers
 White hat hackers:
White hat hackers:
Also referred as Ethical Hacker or sometimes called as Sneakers. A White Hat Hacker mainly focuses on securing corporate Network from outsider threat. They are with good intention who fight against Black Hat.
 Black hat hackers:
Black hat hackers:
Also referred as Cracker. A Black Hat Hacker's intention is to break into others Network, and wish to secure his own machine. They often uses different techniques for breaking into systems which can involve advanced programming skills and social engineering.
 Grey hat hackers:
Grey hat hackers:
They are Skilled Hacker who sometimes act legally and sometime not. In simple word you may call a Grey Hat hacker as Hybrid between White Hat and Black Hat hacker
5. Hacking methods
Phishing Method
Phishing is the method that you are familiar with. You create a Fake Account and ID in yahoo and fool your friends by telling them to send the victim's ID, their own ID and their own Password in your Fake Yahoo Account.
Brute Force Hack
Brute Force Hack is a Hacking which takes much time to get Password of the Victim and it needs a Hacker to learn about Java Scripts and all the non-sense.
Fake Login Hack
Fake Login Hack is the Hacking used by most of you for your goal by creating a Fake Login Page and telling your friends to login there and the Password would come to you. Cookie Steal Hack- Cookie Steal Hack is somewhat similar to Fake Login Hack as you prepare a Cookie Stealer and tell your friends to open your Cookie so that his Password would come to you.
Web Mail Hack
Web Mail Hack is the toughest method to learn for Hacking as it also needs a Hacker to learn about Java Scripts, Computer Tricks and much more and there is also a software for this type of hack.
6. What do ethical hackers do?
An ethical hacker's evaluation of a system's security seeks answers to three basic questions:
· What can an intruder see on the target systems?
· What can an intruder do with that information?
· Does anyone at the target notice the intruder's attempts or successes?
While the first and second of these are clearly important, the third is even more important: If the owners or operators of the target systems do not notice when someone is trying to break in, the intruders can, and will, spend weeks or months trying and will usually eventually succeed.
7. Ethical hacking process
Ethical hacking process involves as follows
ü Preparation.
ü Foot printing.
ü Enumeration and fingerprinting.
ü Identification of vulnerabilities.
ü Attack-exploit the vulnerabilities.
8. The pros of ethical hacking
1. It enables you to find out the problem: Ethical hacking enables you to get beyond the numbers. By this I mean, you can truly figure out what is going wrong, if at all. Are there any breaches in your network? Can a hacker get through them? Which breach is the one that should be seen to and rectified first. Ethical hacking, if done correctly can answer all these questions and more.
2. Helps you build up a risk management program: Ethical hacking is becoming popular because it can help people to set up a proper and informative risk management program. Once you or your company conducts such tests you can make more informed decisions about what changes you need to make in technology. You need to think of ethical hacking in terms of it being a security tool. Test the most crucial systems first such as database or email servers etc.
3. Helps you to think like the enemy: This is probably one of the biggest advantages ethical hacking has to offer. It helps you to think and try and figure out.
9. The cons of ethical hacking
1. It provides only a snapshot of what is happening: This is one of the biggest disadvantages that ethical hacking has. Ethical hacking provides only a snapshot of your company’s security. You may hire a hacker to find out potential threats, but at the end of the day, you are not really safe from these threats. Yes, the hacker may tell you that the security you have in place will ward off new threats. However, no one can predict what these threats might be.
2. Losing data: There is always the chance of data being lost and servers crashing while hacking is being carried out. Anything can go wrong during hacking and you should be prepared for any eventuality. A system that is unstable or overloaded might crash while the testing is being carried out.
3. Being given a false sense of security: This is closely linked to the snapshot you get after ethical hacking is carried out. You may have the best hackers but they might just overlook a critical point. A rogue hacker will then definitely be able to get in and breach the system.
Conclusion
ü Testing is an essential part of any data security program.
ü An ethical hack can reduce the potential exposure of the company to criminal hackers.
ü “It takes a Thief to Catch a Thief”.
ü The periodic ethical hacking and review exercise would enhance the security and mitigate possible loopholes being exploited.
Reference:
Wisegeek.com
Whatisthehacking.com
Wikipedia.com

![clip_image002[4] clip_image002[4]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEiMmAOmwPe1FbXq6qy8ECmah4Bfo-HvuFGGPpdCk75Dvt9JdIvbMlg7fT3p3b83Vf6HaMtY7rp1R9n0ewi3grenTxG9IilU-0fab_Mo5tj006M1XcAYKZCV_NQBslGthkcLFRKg3Vd5e18V/?imgmax=800)